Cells and tissues: types and characteristics - Human histology | Kenhub
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive introduction to the four major tissue types in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. It explores the unique structures and functions of each tissue, including how epithelial tissue forms protective layers, connective tissue supports organs, muscle tissue enables movement, and nervous tissue facilitates communication through neurons. The video emphasizes the significance of these tissues in maintaining the body’s internal functions and movement, offering viewers a clear and engaging overview of human anatomy and its tissue systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 Epithelial tissue covers both internal and external body surfaces and is classified into epithelial tissue proper (for surface lining) and glandular epithelium (for glands).
- 😀 Connective tissue supports and connects different parts of the body, with classifications based on the matrix type: liquid (blood, lymph), semi-solid (loose and dense fibrous tissue), and solid (bone, cartilage).
- 😀 Muscle tissue enables movement and organ motility by converting chemical energy into mechanical energy, allowing actions like running and lifting.
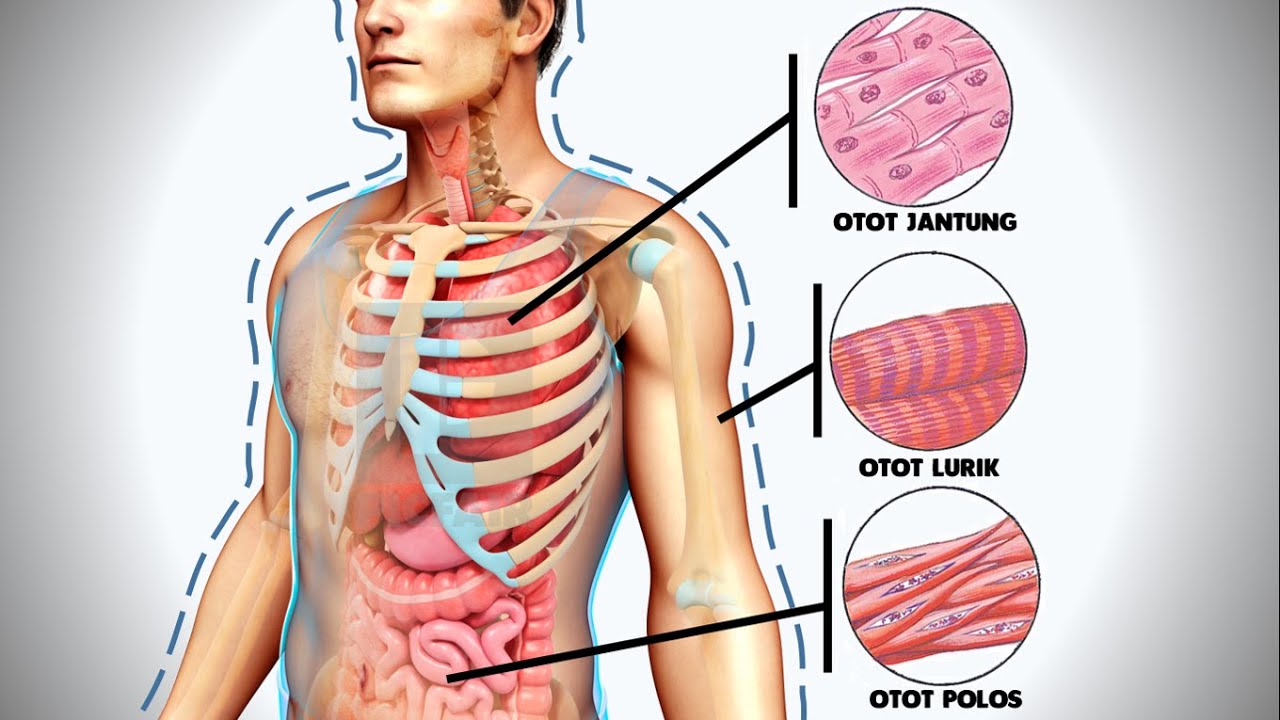
- 😀 Skeletal muscle is responsible for voluntary body movement and posture, is striated, and has multinucleated cells controlled by motor neurons.
- 😀 Cardiac muscle, found only in the heart, is striated, involuntary, has single or dual nuclei, and includes intercalated discs for synchronized contractions.
- 😀 Smooth muscle controls the motility of internal organs (e.g., digestive, urinary, reproductive systems), is spindle-shaped, and non-striated.
- 😀 Nervous tissue comprises neurons and glial cells, enabling communication within the nervous system by transmitting electrical impulses.
- 😀 Neurons are classified as efferent (transmitting signals away from the central nervous system) and afferent (transmitting signals towards the central nervous system).
- 😀 Neurons have a cell body (control center), dendrites (input channels), and axons (transmission cables for signals).
- 😀 Glial cells support neurons by providing protection, insulation, and maintenance, with different types like Schwann cells (PNS) and oligodendrocytes (CNS).
Q & A
What are the four major types of tissue in the human body?
-The four major types of tissue in the human body are epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue primarily serves to line and protect the surfaces of the body, both internally and externally, and forms the ducts and secretory parts of glands.
What are the two types of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue can be divided into two types: epithelial tissue proper (covering and lining epithelium) and glandular epithelium (which forms the ducts and secretory parts of glands).
What are the main categories of connective tissue?
-Connective tissue is categorized into three main types based on the matrix it contains: connective tissue with a liquid matrix (e.g., blood and lymph), semi-solid matrix (e.g., loose and dense connective tissues), and solid matrix (e.g., bone and cartilage).
How do muscle tissues convert energy?
-Muscle tissues convert chemical energy, primarily obtained from food, into mechanical energy. This allows for movements such as lifting, running, and other motor functions.
What are the three types of muscle tissue, and where are they found?
-The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal muscle (found attached to the skeleton), cardiac muscle (found only in the heart), and smooth muscle (found in internal organs such as the digestive and reproductive tracts).
What is the main characteristic of skeletal muscle?
-Skeletal muscle is responsible for voluntary movements and posturing. Its cells, known as muscle fibers, are long, non-branching, multinucleated, and have a striated appearance due to the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments.
How does cardiac muscle differ from skeletal muscle?
-Cardiac muscle, unlike skeletal muscle, has cells with one or two nuclei, forms a three-dimensional network with intercalated discs, and is involuntary, meaning it contracts without conscious control.
What is the structure and function of smooth muscle?
-Smooth muscle has spindle-shaped cells with a single central nucleus and is found in organs like arteries and the digestive tract. It has a non-striated appearance and is involuntary, aiding in internal organ movement without conscious control.
What are the two main types of cells in nervous tissue, and what are their functions?
-The two main types of cells in nervous tissue are neurons, which transmit electrical signals, and glial cells, which support, maintain, and protect neurons.
What are the key features of neurons?
-Neurons have three key features: a cell body that contains the nucleus, dendrites which receive input signals, and an axon that transmits electrical signals to other neurons or target structures.
How are the nervous system and the peripheral nervous system different?
-The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of nerves that transmit signals between the CNS and the rest of the body.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MATERI MARTIKULASI | JARINGAN TUBUH MANUSIA
Media Pembelajaran Jaringan Hewan - Kelas Daring Biologi SMA Kelas XI

Resumão: HISTOLOGIA

Types of Human Body Tissue

Tejidos Básicos del Cuerpo Humano | Tipos y Clasificación | Histología

TECIDOS DO CORPO HUMANO | Resumo de Biologia Enem. Professora Cláudia Aguiar
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)